Since 1965, Thermometrics Corporation has been dedicated to furnishing the industrial community with a smart, yet simple, cost effective solution to temperature measurement. Thermometrics is a manufacturer of analog and digital temperature sensors, RTD's, thermocouples, thermowells, sanitary sensors and accessories for Pharmaceutical, Aerospace, Marine, Petro-Chemical, Food Processing and Utilities.
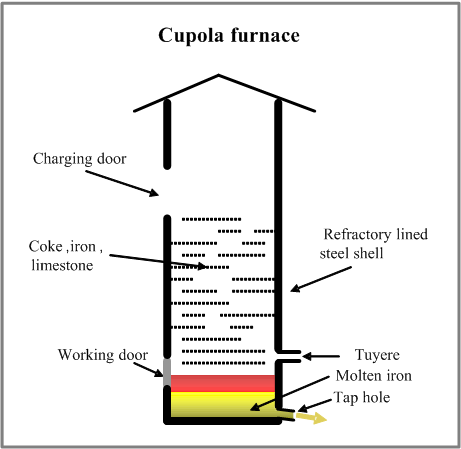
A Cupola or Cupola Furnace is a melting device used in foundries that can be used to melt cast iron, ni-resist iron and some bronzes. The cupola can be made almost any practical size. The overall shape is cylindrical and the equipment is arranged vertically, usually supported by four legs. The overall look is similar to a large smokestack.
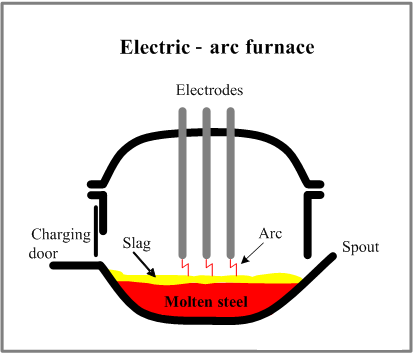
An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats charged material by means of an electric arc. Arc furnaces range in size from small units of approximately one ton capacity (used in foundries for producing cast iron products) up to about 400 ton units used for secondary steelmaking.
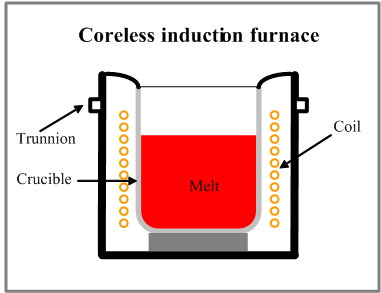
The heart of the coreless induction furnace is the coil, which consists of a hollow section of heavy duty, high conductivity copper tubing which is wound into a helical coil. Coil shape is contained within a steel shell and magnetic shielding is used to prevent heating of the supporting shell. To protect it from overheating, the coil is water-cooled, the water bing recirculated and cooled in a cooling tower. The shell is supported on trunnions on which the furnace tils to facilitate pouring.
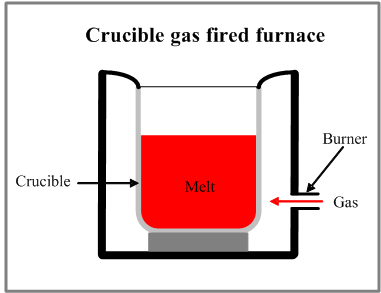
Crucible furnaces are used for melting and holding small batches of non-ferrous alloys. Crucible furnaces are the oldest type of melting furnaces. A refractory crucible filled with the metal is heated through the crucible wall. The Two main types of furnaces are electricity resistance furnace, and the gas (oil) fired furnace. In the gas fired furnaces heat is provided by a burner directed to the crucible. In the resistance furnaces electric heating elements are used as a source of heat.